Google Ads

The race to reach the first page of Google search results is highly competitive. Trying to reach the first page, even with excellent SEO may easily take months or even a year.
This is where paid ads (Pay Per Click) come in. Google Ads (formerly referred to as Google AdWords) is Google’s advertising service that allows businesses to display their ads on Google’s search result pages. The ads usually appear at the top or bottom of a Google SERPs (search engine result pages).
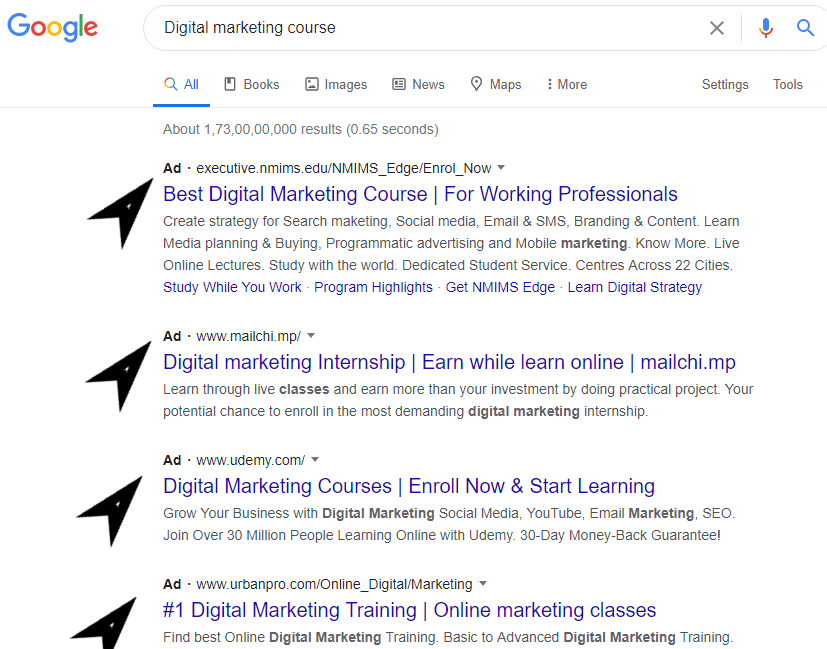
Using Google Ads is a common and effective marketing strategy among businesses looking to get their first online customers. Today we’ll dive into some of the basics on how to use Google AdWords for your business.
(1) Advantages of Using Google Ads
Google Ads is a powerful tool when it comes to advertising a business online. What makes it so great? Below are few of the advantages that businesses enjoy on Google’s paid marketing platform:
(a) Precise Targeting
With Google’s many targeting options, business owners are able to ensure their ad is only displayed to potential customers. Business owners can filter their audience on the basis of geographical location, age, keywords and more. Additionally, they can also choose the time of day when their ads will be displayed to their targeted audience. A common example that a lot of businesses use is running ads only from Monday – Friday from 8 AM to 5 PM. This is due typically due to the fact that businesses are closed or are slower on the weekends. This can help maximize ad spend.
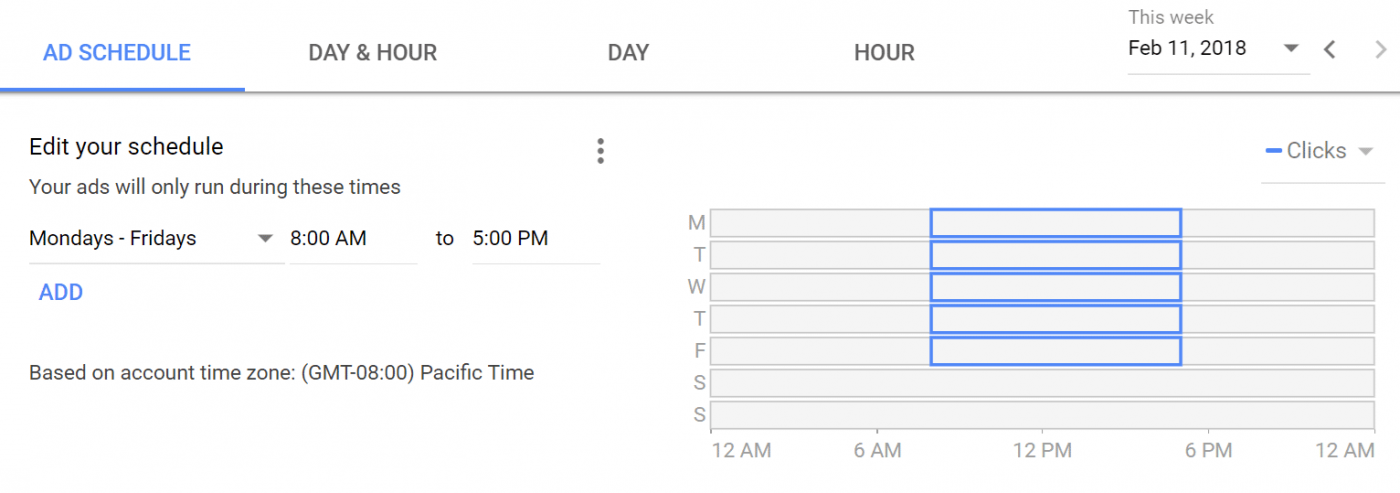
This is especially advantageous for local businesses. Studies show, 50% of mobile users that conducted a local search on their smartphone ended up visiting a store within a day, which gives local businesses an upper hand on catching the crowd’s attention by being on the top of SERPs.
(b) Target Specific Devices
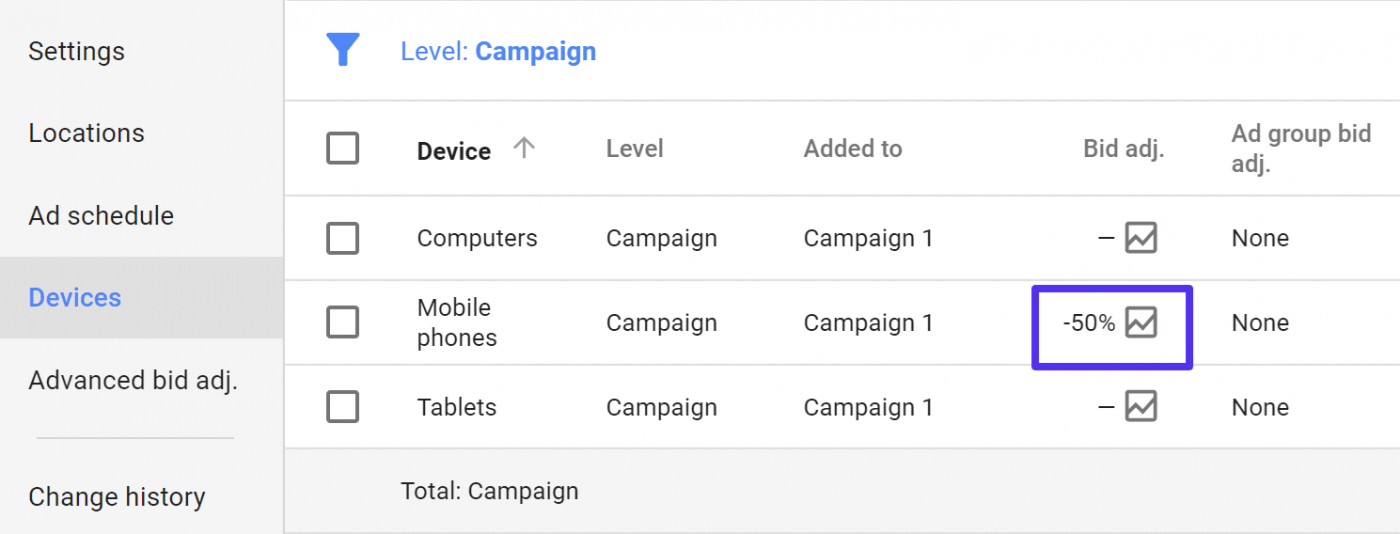
Google Ads allows businesses to choose the kind of devices their ads will be displayed on. For the search network, you can choose between desktops, tablets, and mobile devices. On the display network businesses can even drill down even further and target specific devices like iPhones or Windows. Bid adjustments allow automatically bidding higher or lower on devices that are more likely to convert on your site. Tip: Looking at conversion and ecommerce data in Analytics.
(c) Pay Only For Results
This is arguably the most popular advantage of advertising on Google Ads. With Ads, businesses only pay for the clicks on their ads, instead of impressions. This is called a pay-perclick (PPC) advertising model. This way, businesses save money by only paying when a user has taken action to view their website.
(d) Performance Tracking
Google Ads allows businesses to track the performance of their ads. This means you can track the number of users that view and click your ad. Google Ads also allows you to track the number of users that take the desired action after viewing your website.
(2) Preparing for PPC
Pay Per Click advertising is a powerful tool, but only when it is used smartly. Before you can jump into the process of making your Google Ads account, you must figure out your objectives. While “more sales” might sound like a great objective, online advertising will require you to be more specific.
It is highly unlikely that someone visiting your website for the first time will make a purchase. Online sales are more dependent on making and nurturing a relationship of trust with your consumer. For this reason, there can be a number of objectives for a business to use Google Ads. Such as:
- Generating sales
- Registrations
- Email sign-ups
- Lead Generation
- Enhancing brand awareness and recall value
While it is perfectly fine to have more than one objective, keep in mind that you will have to run different campaigns to achieve different objectives. Apart from identifying your objective, there is another very important prerequisite for advertising on Google Ads, having a landing page.
(a) Landing Page
A landing page is a URL or a webpage on which, a user “lands” when they click on your advertisement. A landing page is a standalone page, distinct from your main website, designed to focus on a specific objective. A great landing page is crucial to the success of your Google Ads campaign. A well designed and optimized landing page will help convert visitors into leads, or even customers. Keep the following things in mind while designing your landing page:
- Focused landing pages: Design individual landing pages for individual offers. A landing page that focuses on multiple objectives might end up confusing your visitors.
- Call to action: Do not forget to include and properly highlight the desired call to action button on your landing page.
- Mobile friendly: With the ever-increasing number of mobile users on the internet, it is crucial to ensure your landing page is mobile friendly.
- Deliver what you promise: Your landing page should deliver any promises made in your ad. For instance, if your ad talks about a discount, make sure the landing page features the said discount.
(3) Setting up Google Ads Account
(a) Step 1: Sign Up
Simply go to the Google Ads website (https://ads.google.com) and sign up with your Google account. If you do not have a Google account, you will have to create one.
Once you have entered the necessary details, you will land on the following page to create your first campaign. Here you can choose your budget, target audience, set your bids, and write your ad copy.
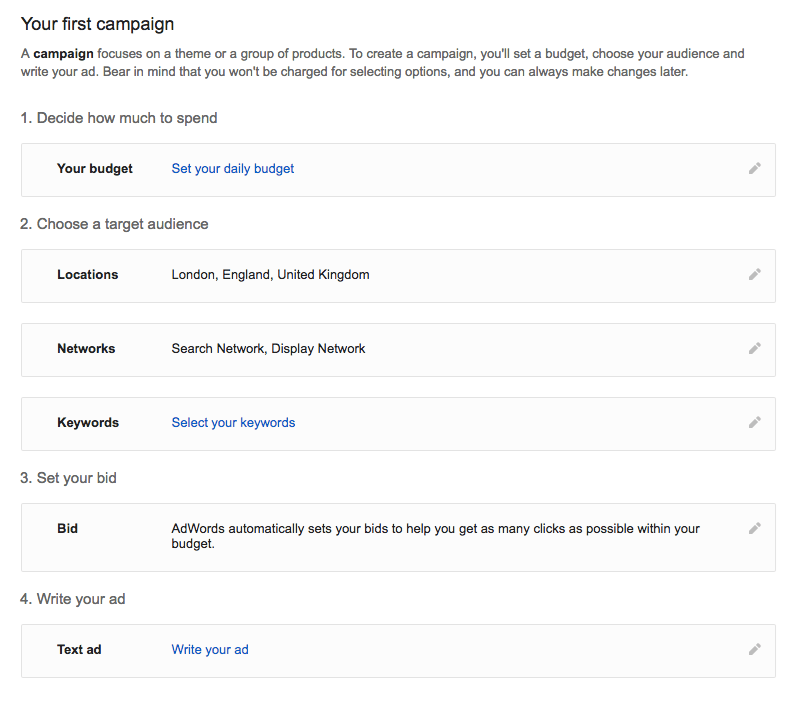
Create New Campaign – once you create a campaign you have to choose one of the below goal options.
- Sales: Drive sales online, in app, by phone, or in store
- Leads: Get leads and other conversions by encouraging customers to take action
- Website Traffic: Get the right people to visit your website
- Product & Brand Consideration: Encourage people to explore your products or services
- Brand Awareness & Reach: Reach a broad audience and build awareness
- App Promotion: Get more installs and interactions for your app
- Create a campaign without a goal’s guidance: Use any available campaign type and construct a campaign step-by-step without a goal’s recommendations
(b) Step 2: Set Your Budget
As you can see, defining a budget is the foremost task on the list. Defining the daily budget will ensure you never cross your expenditure limits. The best way to figure your daily budget is to first understand the number of visitors that your landing page can convert into customers. If you’re just starting out, it’s OK to work with averages.
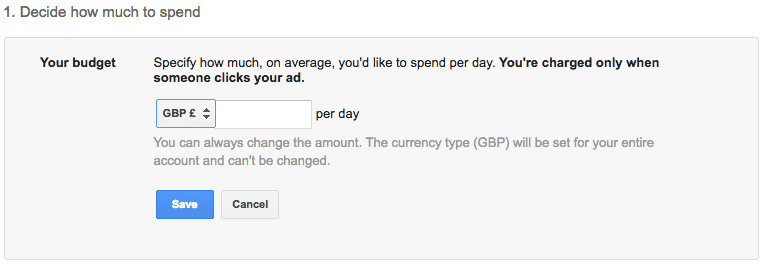
Budget: Enter the average you want to spend each day in Rs.
Shared below are how Google Ads charges:
- Charges and your average daily budget
Internet traffic is like an ocean. Some days, there will be small waves. Other days, there will be great big ones. So, if your ads don’t show up much because of low traffic, then we’ll make up for that by showing them more when traffic’s higher. That’s why we allow up to 2 times the clicks in a day than your average daily budget allows for campaigns that aren’t paying for conversions. This is called overdelivery. And it’s a good thing: if we end up showing your ad too much — to the point where you accrue more costs than your average daily budget allows for over a billing cycle — then we’ll give you a credit for those extra costs.
- Overdelivery and your average daily budget
As we mentioned, you might see that your advertising costs each day are a little higher or lower than what you set for your average daily budget. If you do, don’t worry — over a month-long billing cycle, you won’t be charged more than your average daily budget would’ve allowed for over 30.4 days.
- Let’s explain that number.
Basically, 30.4 is the average number of days in a month (365 days in a year / 12 months = 30.417). Google multiplies your average daily budget by this number so we know what your budget should be over the course of a month. Example Let’s say you set your budget at $5 a day and your billing cycle is 30 days. Over the course of the month, you notice that your charges vary. Some days you’re charged $2, on others you’re charged $10. But at the end of the month, your charges won’t exceed $152 (that’s 30.4 multiplied by your $5 budget). So even though your campaign costs tipped above and fell below your $5 budget from day to day, at the end of the month, you’re still charged no more than what you budgeted. The waves of Internet traffic might make your daily costs go up and down. But at the end of the month, despite those unpredictable waves, you’ll find your costs at right where you expected them to be.
- Check for overdelivery
Sometimes we deliver over your monthly budget. In those cases, we’ll credit the overdelivery cost back.
After you have chosen your desired currency and budget, click on save and move on to the next step.
Ad extensions: Get up to 15% higher clickthrough rate by showing additional information on your ads
- Sitelink extensions
- Callout extensions
- Call extensions
(c) Step 3: Select Your Target Audience
In this step, you get to specify the geographical location of your target audience. This feature ensures your ad is shown only to users that conduct a search using the keywords you’re bidding for (more on this later) and are present in the geographical location specified by you.
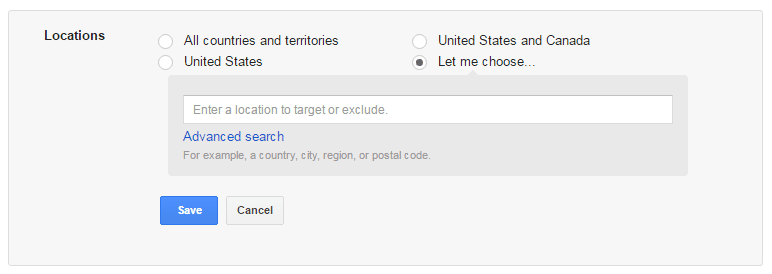
By using the advanced search option, you gain access to “radius targeting”. Radius targeting allows you to target a certain radius from your zip code. Depending upon the nature of your business, you might want to target entire countries, or only cities if you sell something locally. You can even set different bid adjustments per radius targets. For example, perhaps you want to bid higher within a 10-mile radius, but lower within a 30-mile radius.
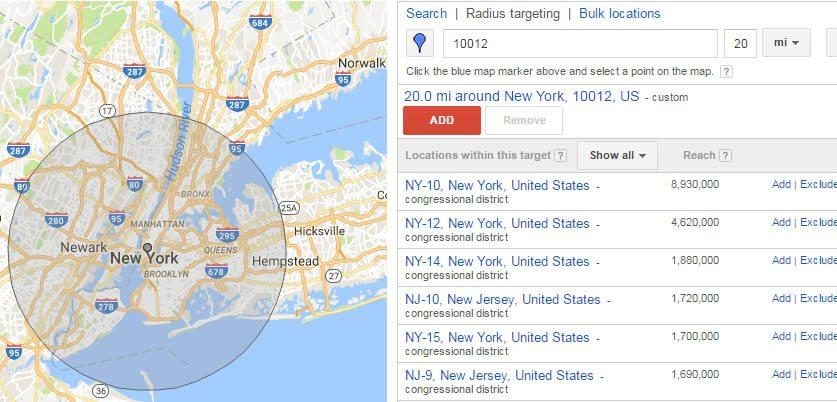
(d) Step 4: Choose A Network
The next step is to choose between Google’s Search Network and Display Network. The Search Network puts your ads on the google SERPs, while the Display Network will display your ad on any website that shows ads.
- Search Network – Ads can appear near Google Search results and other Google sites when people search for terms that are relevant to your keywords
- Display Network – Expand your reach by showing ads to relevant customers as they browse sites, videos, and apps across the Internet
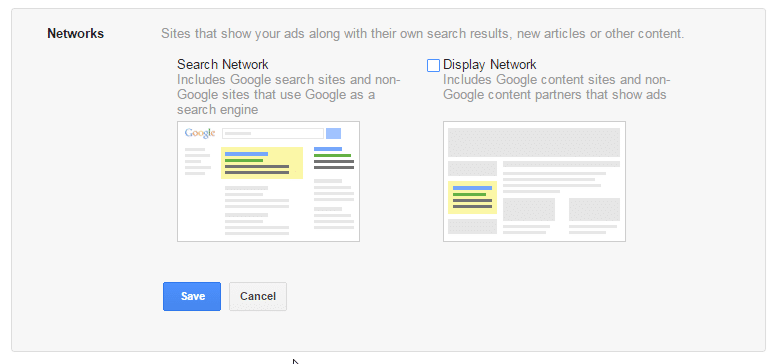
For beginners and small businesses, it is recommended to go with the Search Network as it shows your ads to users that are specifically searching for keywords relevant to your business. Display ads can be great for branding, retargeting, and generally have a lot lower CPC. But they are also not as query oriented.
(e) Step 5: Choose Your Keywords
Keywords are the search terms or phrases a user enters into Google’s search box when they are conducting a search. Google lets you choose about 15-20 keywords that may trigger your ad to appear on the SERP. Don’t worry, you can always add more keywords later on.
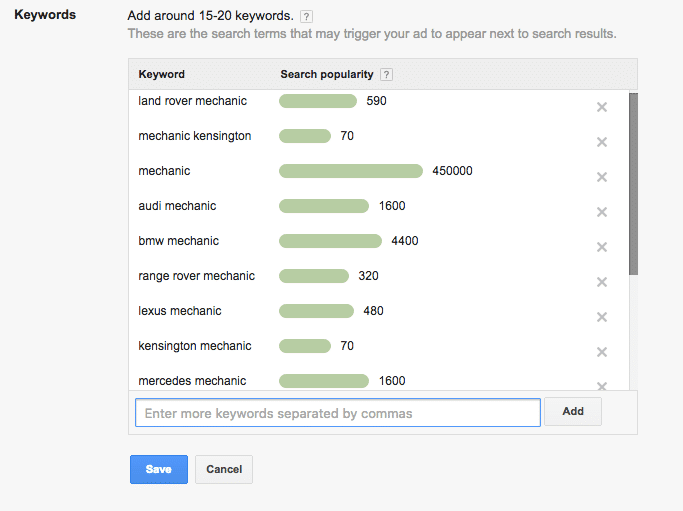
It’s recommended to choose a few keywords that you are sure of bringing results, instead of choosing 20 that you may find sort of relevant. Having said that, also pay attention to the search volumes of the keywords you choose. While it might seem tempting to choose a keyword that has the search volume of 450,000, doing so might not be the best idea. As mentioned earlier, Google Ads works on a bidding system. Keywords with high search volumes are usually extremely expensive to bid for. Choosing more keywords or choosing keywords with high search volume may turn out to be an expensive affair.
Keep your costs in check by choosing a few relevant keywords with moderate search volumes.
Keywords Types and Determining the Right “Keyword Match” There are four keyword match types that determine how you want your ad to be displayed.
Broad match: The broad match is the default setting on Google Ads. According to Google, it “allows your ad to show for searches on similar phrases and relevant variations, including synonyms, singular and plural forms, possible misspellings, stemmings.” Broad match allows to you to reach the widest part of your audience. However, since broad match also shows your ads for synonyms and one part of your keywords, your ad may show up in a lot of irrelevant search results.
For instance, you might be targeting for “fine dining restaurants Manchester”, using broad match, your ad may also show in the results for “pizza in Manchester”.
Broad match modifier: The broad match modifier gives your more control. By simply adding a ‘+’ before a term, you can lock it into place. Only when a search term contains the phrases or words after the ‘+’, will your ad appear in the results. For instance, if you bid for “+fine dining Manchester”, your result will never show for search terms like “pizza in Manchester”.
Phrase match: The phrase match offers even more control to business owners. When you choose phrase match, your ad is only displayed in results for search terms that are in the same order as your chosen keyword. This means, if you choose “fine dining Manchester”, your ad will not show for “Manchester fine dining”. In order to specify phrase match, simply put your keywords between quotations.
Exact match: As the name suggests, this option will ensure your ad only appears when someone searches with a search term identical to your chosen keywords. If you have chosen exact match and your keyword is “fine dining Manchester”, your ad will not even appear for search terms like “best fine dining restaurants in Manchester”. To specify exact match, put brackets around your chosen keywords. (Example: [fine dining Manchester]) Tip: Using exact match can be a safe and slower way to scale your campaigns when just starting out.
Negative keywords: Negative keywords are the terms help you ensure your ad is not shown to irrelevant audiences. This feature of Google Ads comes in handy if you have a product/service that may share keywords with something that is not related.
Tips on KeyWords
You can change the budget as and when you desire by making changes in your Adwords account. Following points to be considered: –
- Is your budget possibly limiting your visibility: You may miss out on potential customers if your daily budget is lower than what is recommended? To change the budget simply visit Campaign Section – Setting tab – to view recommended budget and edit your budget.
- Are you bidding competitively for your most important keywords: Take a look at your most important keywords Take a look at your most important keywords – do they have an Avg. Position between 1 and 8. If your Avg. Position is below 8 you Ad may not feature on the 1st page of the google search results. By increasing the bid for these keywords you may be able to improve you position.
- Updating you keywords: Looking out for following –
>Do most of your keywords consist of 2-3 words (having just one word makes it too generic while having 4-5 words makes it too specific – you have to get the right balance).
>Do you have keywords with CTR of less than 1% (may be an indicator that the keyword is too generic OR that the ad does not speak to it).
>Check out the ‘Keyword Tool’ which gives you suggestions on keywords related to your products and services.
(f) Step 6: Set Your Bid
As mentioned earlier, Google Ads uses a bidding model. A bid is the amount of money you are willing to pay for every person that clicks on your ad. If you and your competitor are bidding for the same keyword, and you are willing to pay more per click, your ad will show higher than theirs.
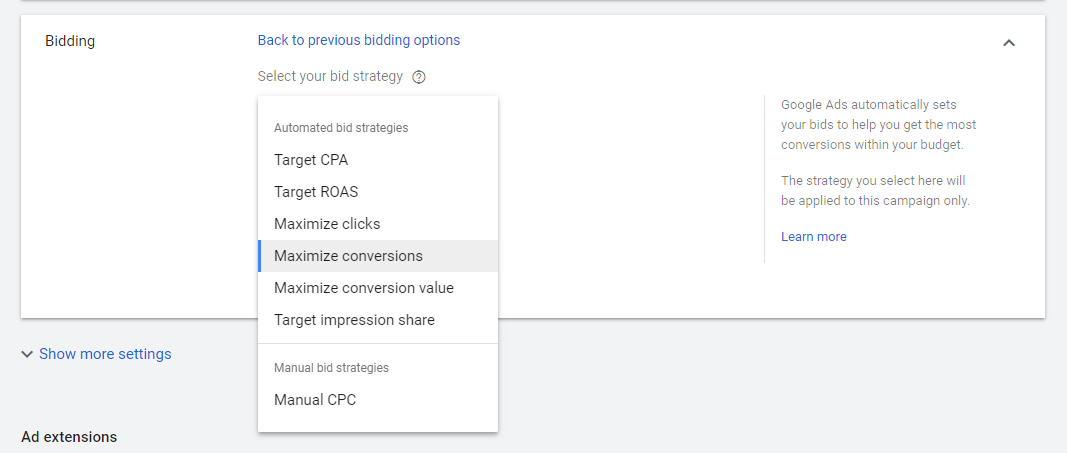
In bidding options – you are presented with two options. This first one “automatic bid strategies” lets Google set your bid amount to maximize the returns of your budget. If you would rather set your bid manually, we suggest doing some research using Google’s Keyword Planner. If you’re just starting out you might want to start with automatic bids until you get familiar with the AdWords system. However, setting bids manually can usually be more costeffective. Although sometimes this also requires additional ongoing maintenance.
Google Ads offers several automatic bid strategies that are tailored to different types of campaigns. Depending on which networks your campaign is targeting, and whether you want to focus on getting clicks, impressions, conversions, or views you can determine which strategy is best for you. Determine a bid strategy based on your goals. Each bid strategy is suited for different kinds of campaigns and advertising goals. For the purposes of bidding, you’ll want to consider five basic types of goals, along with your current campaign settings.
- If you want customers to take a direct action on your site, and you’re using conversion tracking, then it may be best to focus on conversions. Smart Bidding lets you do that.
- If you want to generate traffic to your website, focusing on clicks could be ideal for you. Cost-per-click (CPC) bidding may be right for your campaign.
- If you want to increase brand awareness—not drive traffic to your site—focusing on impressions may be your strategy. You can use cost-per-thousand viewable impressions (vCPM) bidding to put your message in front of customers. You can also use a Target Search Page Location or Target Outranking Share strategy to maximize visibility.
- If you run video ads and want to increase views or interactions with your ads, you can use cost-per-view (CPV) or cost-per-thousand impressions (CPM) bidding.
- If you run video ads and your goal is to increase product or brand consideration you can use cost per view (CPV).
Focus on conversions with Smart Bidding
If you want to focus on conversions, consider using Smart Bidding to take much of the heavy lifting and guesswork out of setting bids. Smart Bidding is a set of automated bid strategies that uses machine learning to optimize for conversions or conversion value in each and every auction—a feature known as “auction-time bidding.” It also factors in a wide range of auctiontime signals such as device, location, time of day, language, and operating system to capture the unique context of every search. Below are the Smart Bidding strategies you can use.
- Target cost per action (CPA): If you want to optimize for conversions, you can use Target CPA to help increase conversions while targeting a specific cost per action (CPA).
- Target return on ad spend (ROAS): If you want to optimize for conversion value, you can use Target ROAS to help increase conversion value while targeting a specific return on ad spend (ROAS).
- Maximize Clicks: This is an automated bid strategy. It’s the simplest way to bid for clicks. All you have to do is set an average daily budget, and the Google Ads system automatically manages your bids to bring you the most clicks possible within your budget.
- Maximize Conversions: If you want to optimize for conversions, but just want to spend your entire budget instead of targeting a specific CPA, you can use Maximize Conversions.
Maximize conversions is the Default option shown
Maximize conversions automatically sets bids to help get the most conversions for your campaign while spending your budget. It uses advanced machine learning to automatically optimize bids and offers auction-time bidding capabilities that tailor bids for each and every auction.
Before you can set up a Maximize conversions bid strategy, you’ll need to set up conversion tracking. How it works – Using historical information about your campaign and evaluating the contextual signals present at auction-time, Maximize conversions bidding automatically finds an optimal bid for your ad each time it’s eligible to appear. Google Ads sets these bids to help get the most conversions for your campaign while spending your budget.
Before switching to Maximize conversions: Check your average daily budget amount. Maximize conversions will try to fully spend your average daily budget, so if you’re currently spending much less than your budget, Maximize conversions could increase spend significantly.
Check your ROI goals. If you have an ROI goal for your campaign, such as a target costper-action (CPA) or return on ad spend (ROAS), you may want to switch to a Target CPA or Target ROAS bid strategy. Like Maximize conversions, these strategies automatically set bids for each auction, but the goal will be to achieve the average CPA or ROAS target you set, rather than spending your full budget to maximize conversions.
- Maximize Conversion Value: If you want to optimize for conversion value, but just want to spend your entire budget instead of targeting a specific ROAS, you can use Maximize Conversion Value.
- Target impression share is a Smart Bidding strategy that automatically sets bids with the goal of showing your ad on the absolute top of the page, on the top of the page, or anywhere on the page of Google search results. Google Ads automatically sets your bids to show your ad, based on your placement settings. For example, if you choose an Impression Share target of 65% on the absolute top of the page, Google Ads will automatically set your CPC bids to help show your ads on the absolute top of the page 65% of the total possible amount of times they could show.
>Target Search Page Location: This is an automated bid strategy that automatically sets your bids to help increase the chances that your ads appear at the top of the page, or on the first page of search results. Learn more About Target Search Page Location bidding.
>Target Outranking Share: This is an automated bid strategy that lets you choose a domain you want to outrank so that your ad is displayed above that domain’s ads, or shows when that domain’s ad does not. You can set how often you want to outrank that domain, and Google Ads automatically sets your Search bids to help meet that target. Learn more About Target Outranking Share bidding.
Manual CPC bidding:
This lets you manage your maximum CPC bids yourself. You can set different bids for each ad group in your campaign, or for individual keywords or placements. If you’ve found that certain keywords or placements are more profitable, you can use manual bidding to allocate more of your advertising budget to those keywords or placements.
(g) Step 7: Write Your Ad
Writing your ad is arguably the most critical part of this process. We suggest you give it real thought and make it really compelling. Your message should clearly communicate your offer in such a way, that it convinces a user to click on your ad and visit your website. Here are a few tips to get you started:
Copywriting Best Practices
- Keep it short: There’s not a lot of space for text. So keep your message to the point.
- The headline is crucial: The headline of your ad is the first thing a user will encounter. Make sure it calls out to them and convinces them to click on the ad.
- Have a clear call to action: A clear call to action tells the user what you want them to do.
Anatomy of an ad:
- Headlines: Google Ads allows for up to three headlines to be included in an ad, each accommodating 30 characters. Make sure you use this limited space wisely. Additionally, it is recommended to include at least one of your chosen keywords in your headlines.
- Description: Google Ads allows for up to two description spaces to be included in an ad, each accommodating 90 characters. Use it to convey your message to the user clearly. If possible, include any offers or discounts in this section to ensure the user clicks on your ad. Additionally, triple check for spelling and grammatical mistakes.
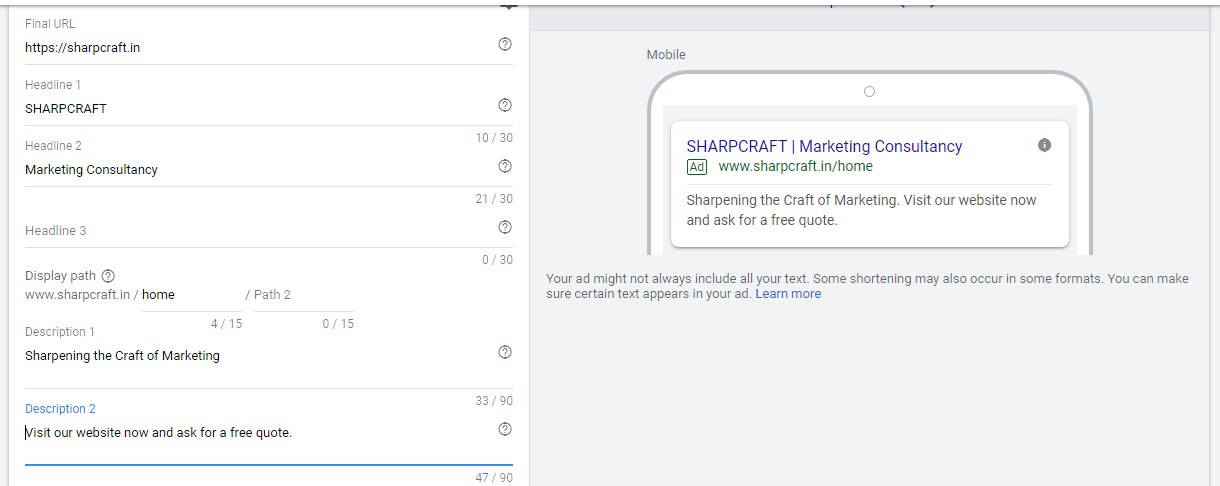
(h) Step 8: Create your Ad
Once you are done writing your ad, click on the “save” button and continue to the last step of the process. In this section, Google will ask you about your business and payment information. You will be charged when you have exhausted your set budget, or 30 days later, whichever comes first.
(4) Running Multiple Ads
As previously mentioned, it is advisable to run multiple ads to focus on various objectives. This can be easily done by running multiple campaigns at once. You can then find out which ones convert best for your business.
(a) Structure Your Account
The structure of your account in Google Ads is critical to the efficiency and success of your paid search campaign.
So you have your keywords, you have the list of keywords that you’re buying, and then you have the ad that you want to show when somebody types in one of those keywords. Now you want to group together the keywords for which you want your ad to be displayed, so that you can create highly relevant ad copy for these keywords and increase the likelihood that the searchers are going to click through.
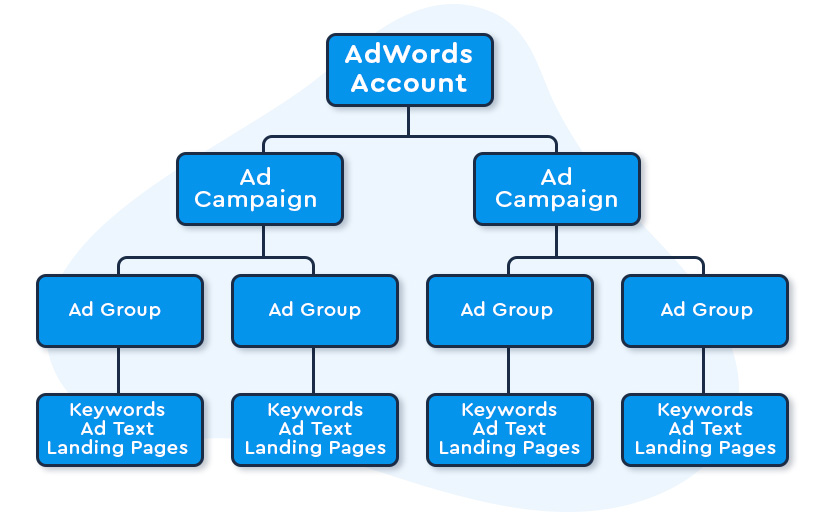
For instance, for a sportswear store, two campaigns can be created one for Shoes and one for Polo Shirts. While one ad group may be dedicated to Tennis Shoes and Walking Shoes another ad group can be dedicated to Polo Shirts.
You can do this by creating a grouping of related keywords in what is called an “ad group.” So let’s say you have the keywords ‘tennis shoes,’ ‘best tennis shoes,’ and ‘shoes for tennis.’ You can create a ‘Tennis Shoes’ ad group, put those keywords in the ad group, and create an ad that is closely targeted to those keywords. Then you can set up more ad groups ‘Walking Shoes’.
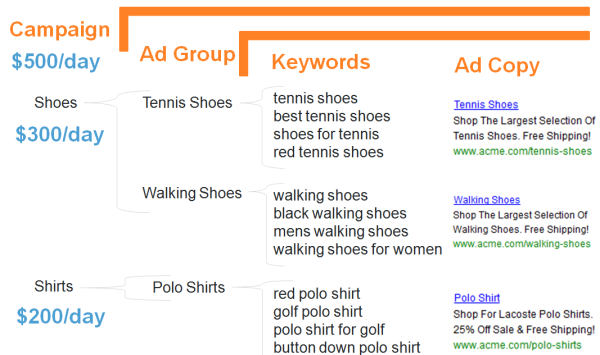
(b) Setting the budget
All the 3 ad groups can be included in the same campaign. However the ad groups in a single campaign will share the same budget and location and device targeting settings. If you are looking to target multiple locations or devices, you will have to create separate campaigns.
When you pay Google for your PPC campaign, you don’t whip out your credit card every time someone clicks on your ad. Instead, you set a daily budget on the campaign level. So for each campaign, you can dictate how much money Google can spend on those ad placements per day. For example, you can say you want to spend $300/day on your shoe campaign and $200/day on your shirt campaign, and Google won’t exceed those amounts.
(5) Campaign Evaluation
As mentioned earlier, one of the biggest advantages of using Google Ads is its tracking capabilities. Using these, you will be able to determine if the ad you just created is performing well.
In order to do that, the first step is to select a conversion source. For small businesses the two most common conversion areas are:
- Websites: When a customer clicks on your ad, visits your landing page, and performs the desired action.
- Phones: When a mobile user calls you on the phone number mentioned in your ad or by clicking on the call button on your website or landing page.
The first thing you’ll want to do is set up a Google Analytics goal on your website and then follow these additional instructions for setting up Google Ads conversion tracking (WordPress, Woocommerce, and Easy Digital Downloads). You can also track phone conversions on your ads. Tip: If your business relies heavily on phone calls, it’s also recommended to sign up for a third-party call reporting software such as CallRail. This has an easy integration with WordPress and Google Ads.
(6) Google’s Quality Score
Google also tracks how your ads are performing, and uses this information to determine where your ad will show on the search result page. Using the following factors as reference, Google assigns a Quality Score (QS) to each of your keywords:
- Landing page relevance: The relevance of the keyword to the content present on your landing page.
- Expected click-through-ratio: The likeliness of a user clicking on your ad after searching for the keyword.
- Ad relevance: The relevance of your ad to the keyword.
Check the quality score of your keywords by adding the “quality score” column under the keywords tab of your AdWords account.
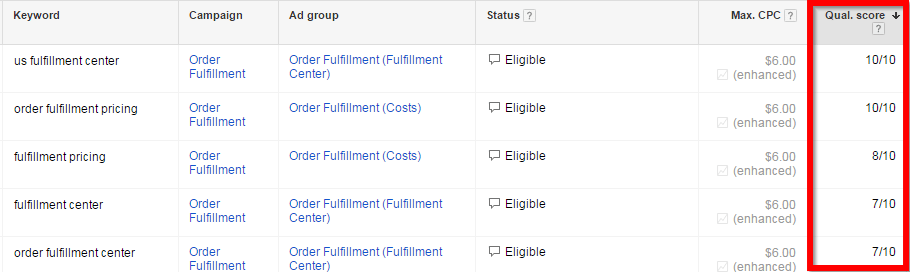
The quality score not only helps determine the positioning of your ad, it also affects the bidding process and what you pay per click. To determine the position of your ad, Google will multiply the bid amount with your quality score. For instance, for a certain keyword, if your quality score is 0.7, and you make a $1 bid, your ad will be placed below your competitor whose quality score is 0.4 and bid is $2.
A 7/10 Quality Score is the recommended number and is sufficient. Going above 7 is great but not always achievable and may not be worth the effort. Anything below 7 is a sign that something is wrong and should be worked on.
