Search Engine Basics

Search engines catalogue the Internet to help connect searchers with exactly what they’re looking for. That makes them a great marketing tool. So where did search engines come from? One of the earliest search engines was a program called Archie, which debuted in 1990 and allowed people to access and search file names— basically the names of the web pages. But, Archie couldn’t tell you what was on those pages.
Fast forward a few decades, and search engines like Google, Bing, Yahoo!, Ask.com, AOL, Baidu, and Yandex have come a long way. These search engines use incredibly sophisticated computer programs to sort through a massive number of web pages.
Most search engines basically work in the same way. When a person wants to find something, they type in a word or phrase, called a search query. Then, the search engine compares that query to its catalogue of web pages, pulling out the best matches to show the searcher. These are displayed on a search results page.
Their goal, is to create the most relevant list of results possible, to help searchers find what they are looking for. The results page includes links to websites, but you might also see local business listings, items for sale, advertisements, images, maps, videos and more. So how does this apply to you?
Why? Because the words entered into the search engine indicate the searcher is interested in your products and services, right now. Search is a great place to be because it’s a way to target people who are already looking for you.
(1) How Search Engines Work
Search engines examine all the pages on the World Wide Web, categorise them and put them into a logical order when you search for something. Each search engine uses their own software programs, but the way they work is pretty similar. They all perform three tasks – Crawling, Indexing and Ranking. First, they examine content they learn about and have permission to see (that’s called crawling). Second, they categorise each piece of content (that’s called indexing). And third, they decide which content is most useful to searchers (that’s called ranking). Let’s take a closer look at how these work.
(a) Crawling
Search engines “crawl” the Internet to discover content, like web pages, images and videos. Each search engine uses computer programs called “bots” (short for robot), “crawlers” or “spiders” to make their way through the pages. The bots hop from page to page by following links to other pages. These bots never stop; their sole purpose is to visit and revisit pages looking for new links and new content to include in the index.
(b) Indexing
Indexing is the second part of the process. The index is a gigantic list of all the web pages and content found by the bots. The search engine uses this index as the source of information displayed on the search results pages.
But, not everything the bots find makes it into a search engine’s index. For example, search engines may find multiple copies of the exact same piece of content, located on different websites. How is that possible? Well, imagine you’re not searching for a coffee shop, but a coffeemaker. You might notice that the top-of-the-line FruitJuicerT2000 has the same word-for-word description on the websites of many major retailers. The description might have been provided by the manufacturer… but now the search engine has decisions to make: which version to keep in the index? There’s no need for hundreds of duplicates, so it’s unlikely that every page will be added. So if you own a website that’s selling coffeemakers, you’re likely better off writing your own description of the FruitJuicerT2000.
When you type in a search, the engine compares the words and phrases you use to its index, looking for matching results. Let’s say, for example, the search engine finds 230 million matching results.
(c) Ranking
Now it’s time for the last part of the search engine’s task: ranking. The way search engines rank pages is top secret—it’s their ‘special sauce.’ There are hundreds of ways search engines determine rank, including things like the words on the page, the number of other websites linking to it, and the freshness of the content. But no matter what formula they use to determine rank, the goal remains the same: to try to connect the searcher with what they are looking for.
(2) Optimise your pages
How Search Engines see the web In simple terms, when you ask a search engine to find something, it looks through a huge list of previously indexed pages, called “the index,” and pulls out relevant results based on what you’re looking for.
Pages make it into “the index” only after the search engine has determined what they’re about. That way, it can file them in exactly the right place amongst the other pages, and find them the next time a search relates to their content.
By knowing “how” a search engine decides what a page is about, you can “optimise” your pages to make sure they show up in the search results of people looking for websites just like yours.
(a) HTML
Let’s say you own a juice shop, and you’ve got a website to promote it. When you look at a page on the site you see the imagery and text content. But when a search engine looks at the same page, in addition to seeing what you see on your screen, it also sees the code behind it, called HTML (HyperTextMarkupLanguage). Specific parts of this code help the search engine understand what the web page is all about. And knowing which parts are important can help you to optimise your site. First, the title of the page in the code. In this example, you can see the title in the tab at the top: “Juice Shop.” The search engine sees the title enclosed in a piece of code called a title tag. Many websites can be edited using tools that handle all the HTML coding for you – that’s called a content management system, or CMS. If you use a CMS to make changes to your website, there’s probably a place to add this title, too. You can help the search engine index your page properly by making sure your page title accurately describes its content. That way it can show up in relevant searches.
(b) Text
The next thing you’ll want to think about is the page’s text. Think about who you want to visit your page, and what words they’re using to describe your products and services. Do they talk about fresh grape juice? Fresh grape juice with pulp – these are probably the terms they’re also using to search. Try to speak the language of your customers when you write your content. Because this can help ensure they’ll find your pages when they search.
(c) Alternate Text
Finally, let’s talk about the page’s images. Search engines won’t see the mouth-watering photos of your juice creations in the same way we do – which is a shame. But what they will see is the code behind it. To help search engines identify the image, give it a descriptive name. For example, image.jpg is not a great file name for search engines. Whereas, something that describes exactly what’s in the picture, like fresh-grape-juice.jpg, is.
You can even take it one step further by adding “alternative text” in the code with your image. Known as an “Alt tag,” it describes the image, which is useful for people using web browsers that don’t display images, or for people with visual impairments who use software to listen to the content of web pages. In the HTML , the ALT tag will appear something like this: src=”http://www.example.com.com/fresh-grape-juice.jpg ” alt=”Fresh Grape Juice”>
So remember: Use descriptive, unique titles for each page on your site. Write for your customers, but remember to include important words and phrases that can help search engines understand what your pages are all about. And don’t forget to name image files with descriptive words and include alternative text.
(3) Popular Search Engines

Which are the 10 most popular search engines in the World? Besides Google and Bing, there are other search engines that may not be so well known but still serve millions of search queries per day.
Google is not the only search engine available on the Internet today, in fact, there are a number of search engines that want to take Google’s throne but none of them is ready (yet) to even pose a threat.
Recent statistics (updated April 2020), show that Google is the most popular search engine Worldwide with a stunning 87.35% market share.
According to statistics from netmarketshare, statista and statcounter, the top 5 search engines worldwide in terms of search engine market share are:
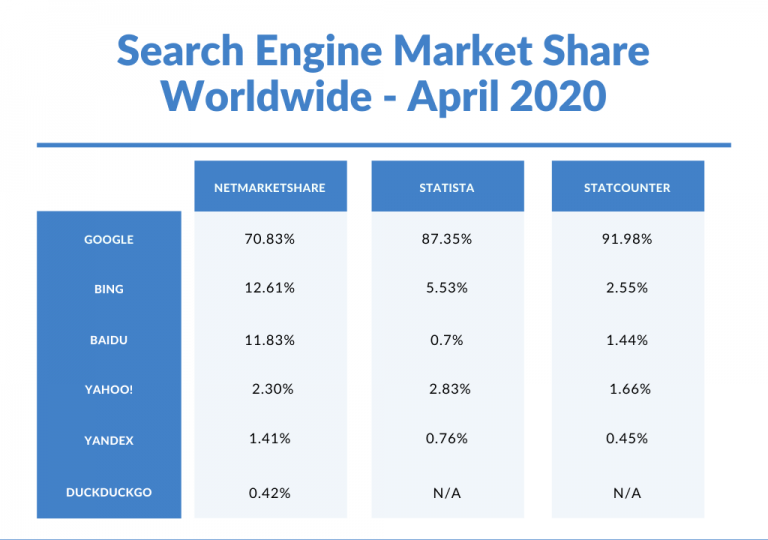
- Google is the best search engine with a worldwide market share between 70.83% and 91.98%.
- Bing search market share is between 2.55% and 12.61%. This places Bing as the best alternative search engine to Google.
- Yahoo market share is between 1.66% and 2.83%.
- Baidu has a global market share between 0.7% and 11.83% but it is the most popular search engine in China.
- Yandex, Russian’s most popular search engine has a global market share between 0.45% and 1.41%.
- DuckDuckGo market share is around 0.42%.
(a) Google
The search engine giant holds the first place in search with a stunning difference of 76% from second in place Bing.
As you can see in the table above, Google is dominating the market in all countries on any device (desktop, mobile, and tablet).
What made Google the most popular and trusted search engine is the quality of its search results. Google is using sophisticated algorithms to present the most accurate results to the users. Google’s founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin came up with the idea that websites referenced by other websites are more important than others and thus deserve a higher ranking in the search results.
Over the years the Google ranking algorithm has been enriched with hundreds of other factors (including the help of machine learning) and still remains the most reliable way to find exactly what you are looking for on the Internet.
(b) Bing
Bing is Microsoft’s attempt to challenge Google in search, but despite their efforts, they still did not manage to convince users that their search engine can be a reliable alternative to Google.
Their search engine market share is constantly below 6%, even though Bing is the default search engine on Windows PCs.
Bing originated from Microsoft’s previous search engines (MSN Search, Windows Live Search, Live Search) and according to Alexa rank is the #30 most visited website on the Internet.
(c) Yahoo
Yahoo is one of the most popular email providers and its web search engine holds the third place in search with an average of 2% market share.
From October 2011 to October 2015, Yahoo search was powered exclusively by Bing. In October 2015 Yahoo agreed with Google to provide search-related services and until October 2018, the results of Yahoo were powered both by Google and Bing. As of October 2019, Yahoo! Search is once again provided exclusively by Bing.
Yahoo is also the default search engine for Firefox browsers in the United States (since 2014).
Yahoo’s web portal is very popular and ranks as the 11 most visited website on the Internet (According to Alexa).
(d) Baidu
Baidu was founded in 2000 and it is the most popular search engine in China. Its market share is increasing steadily and according to Wikipedia, Baidu is serving billions of search queries per month. It is currently ranked at position 4, in the Alexa Rankings.
Although Baidu is accessible worldwide, it is only available in the Chinese language.
(e) Yandex
According to Alexa, Yandex.ru is among the 30 most popular websites on the Internet with a ranking position of 4 in Russian.
Yandex presents itself as a technology company that builds intelligent products and services powered by machine learning. According to Wikipedia, Yandex operates the largest search engine in Russia with about 65% market share in that country.
(f) DuckDuckGo
According to DuckDuckGo traffic stats, they are serving on average 47 million searches per day but still their overall market share is constantly below 0.5%. Unlike what most people believe, DuckDuckGo does not have a search index of their own (like Google and Bing) but they generate their search results using a variety of sources.
In other words, they don’t have their own data but they depend on other sources (like Yelp, Bing, Yahoo, StackOverflow) to provide answers to users’ questions. This is a big limitation compared to Google that has a set of algorithms to determine the best results from all the websites available on the Internet.
On the positive side, DuckDuck Go has a clean interface, it does not track users and it is not fully loaded with ads.
(g) Ask
Formerly known as Ask Jeeves, Ask.com receives approximately 0.42% of the search share. ASK is based on a question/answer format where most questions are answered by other users or are in the form of polls.
It also has the general search functionality but the results returned lack quality compared to Google or even Bing and Yahoo.
(h) Aol
According to netmarketshare the old-time famous AOL is still in the top 10 search engines with a market share that is close to 0.05%.
The AOL network includes many popular web sites like engadget.com, techchrunch.com, and huffingtonpost.com. On June 23, 2015, AOL was acquired by Verizon Communications.
(i) WolframAlpha
WolframAlpha is different than all the other search engines. They market it as a Computational Knowledge Engine which can give you facts and data for a number of topics.
It can do all sorts of calculations, for example, if you enter “mortgage 2000” as input it will calculate your loan amount, interest paid, etc. based on a number of assumptions.
(j) Internet Archive
archive.org is the internet archive search engine. You can use it to find out how a web site looked since 1996. It is a very useful tool if you want to trace the history of a domain and examine how it has changed over the years.
Though these are the 10 best and most popular search engines on the Internet today. Going forward, as far as the first places are concerned, Google and Bing will continue to hold the lead positions in the years to come.
